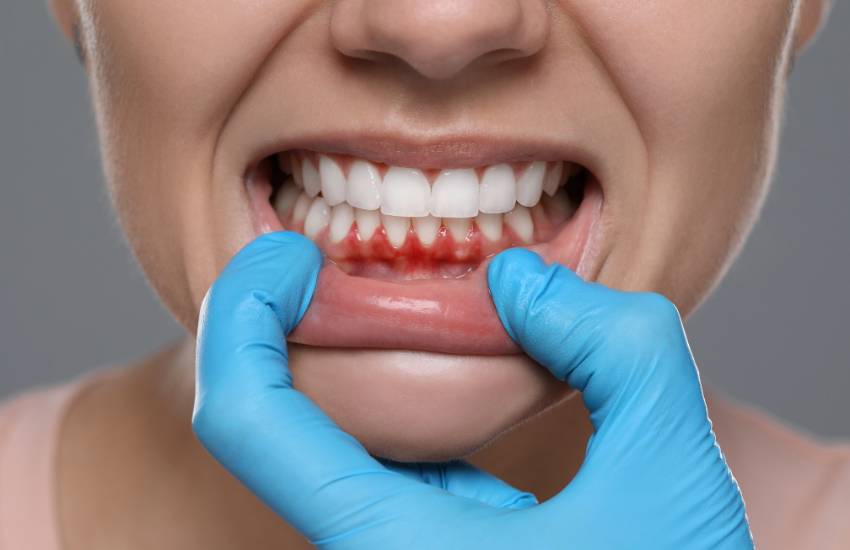
Bleeding Gum

Call Us Today
What is Bleeding Gum?
Bleeding gums refer to bleeding from the gums, typically while brushing teeth, flossing, or eating crunchy foods. It is the cardinal symptom of gum diseases like gingivitis (mild gum inflammation) and periodontitis (advanced gum infection). Bleeding can also result from aggressive brushing, ill-fitting dentures, hormone changes, diabetes, leukaemia, blood thinners, and vitamin deficiency.
Mild and infrequent gum bleeding is usually not a major concern. But frequent bleeding gums and gums bleeding for no reason indicate an underlying dental/health issue needing treatment.
Why are my gums bleeding?
There are several reasons why your gums might bleed. In most cases, oral health-related issues cause it. But it can also be a symptom of other health conditions.
Poor oral hygiene
Smoking
Periodontitis (moderate to advanced gum disease)
Trench mouth (severe gum disease)
Symptoms of Bleeding Gums
Some symptoms of bleeding gums are as follows:
Gums bleeding when brushing or flossing your teeth. This is one of the most common symptoms of gum issues.
Gums appear red, swollen, and tender to touch.
Receding gums is a symptom where gums pull back from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth surface. This can increase sensitivity.
Advanced gum disease may cause teeth to become loose or unstable in their sockets. This occurs as the disease damages the tissues supporting the teeth.
You may experience a metallic taste in your mouth, which is an unpleasant symptom.
Inflamed gums that bleed often look shiny, smooth, and bright red due to increased blood flow to the area.
Gums affected by disease may feel soft, swollen, and spongy.
Pus discharge is a symptom of advanced infection causing abscess in the gums.
Diagnosis of Bleeding Gums
To diagnose a gum disease, dentists do a thorough checkup. All these tests help dentists correctly diagnose gum diseases and determine their severity. This helps them plan the right treatment. The diagnosis includes:
- Medical history: Dentists ask about symptoms, medications, and health conditions to understand likely causes.
- Dental examination: This involves checking for dental plaque, swollen gums, gum recession, loose teeth, and other signs of gum disease.
- Gum probing: This examination involves testing gum pockets around teeth using a periodontal probe to check for detachment from the tooth.
- Dental X-rays: Doctors assess bone loss around teeth and damage due to gum disease.
- Blood tests: These tests help diagnose blood disorders, vitamin deficiency, diabetes, leukaemia, and other systemic causes.
Treatment of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums treatment involves addressing the underlying issue. A few bleeding gum treatment options include:
- Professional cleaning: This procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar deposits, and smoothing of rough tooth surfaces. It’s typically done every 6 months.
- Scaling and root planing: It is a deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar below the gum line and smooth root surfaces.
- Medications: Medications, such as antibacterial mouth rinses, antibiotic gels, or antibiotics, are commonly prescribed for gum infections and bleeding gums.
- Gum treatments: Gum grafts and flap surgery are recommended, depending on the severity of the gum disease.
- Addressing underlying causes: Managing diabetes, adjusting medications, taking supplements for vitamin deficiency, denture adjustments, etc, can also help manage gum bleeds.
If you’ve already developed pain because of your wisdom teeth, then extraction can often ease discomfort almost immediately and get you back on track to better oral health.
FAQs
Ans: Bleeding gums can be caused by a variety of factors, including gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis), brushing too hard, poor oral hygiene, vitamin deficiencies, or certain medical conditions. It’s important to identify the underlying cause to address the issue effectively.
Ans: Preventing bleeding gums involves maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. Regular dental checkups can also help prevent gum disease and identify issues early.
Ans: Home remedies for bleeding gums include rinsing with warm salt water, using aloe vera gel to soothe inflammation, and ensuring a balanced diet rich in vitamin C. However, these remedies should complement professional dental care and not replace it.
Ans: You should see a dentist if your gums bleed frequently, if the bleeding is accompanied by pain or swelling, or if it does not improve with improved oral hygiene. Persistent bleeding could be a sign of gum disease or other underlying health issues that need professional treatment.
Ans: Yes, bleeding gums can sometimes indicate serious health conditions such as vitamin deficiencies, blood disorders, or systemic diseases. It’s important to have any persistent or severe bleeding evaluated by a dentist to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Ans: Improving your oral hygiene involves brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, using an antibacterial mouthwash, and scheduling regular dental checkups. Proper technique and routine care help prevent plaque buildup and gum disease.

